Mars has been the subject of humanity's next frontier when it comes to space exploration and space travel in recent decades.
Astronomers and space enthusiasts have focused more on Mars than any other planets in our solar system, with the hopes of finding signs of life and further understanding the history of the universe.
The Mars Exploration Program
For almost 30 years, the National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA) has explored Mars and even sent rovers under its Mars Exploration Program.
This is to study geological and climate features of the Red Planet.
It found evidence that it once resembled an environment similar to Earth, due to the presence of now-depleted water and atmosphere that could possibly sustain life.
Mars contained marks from the remnants of the past since it has also been vulnerable to impacts from asteroids, meteoroids, or comets for billions of years.
In fact, the European Space Agency (ESA) recently discovered crater marks from ancient space object impacts on the planet never seen before.
The discovery of the unknown crater scars from prehistoric impacts could further help astronomers understand the history of Mars, in terms of its position since the formation of the Sun and the rest of our neighboring planets 4.6 billion years ago.
Unknown Crater
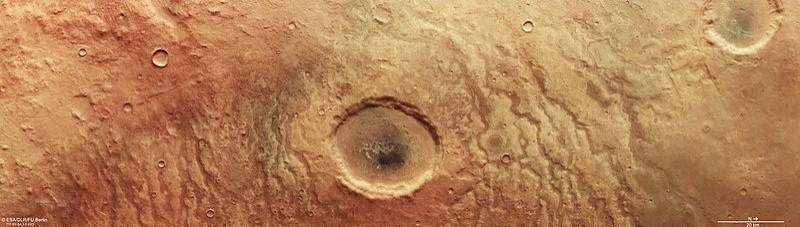
Prior to its discovery, a massive crater in the Aonia Terra region of Mars was unknown until the ESA captured an image of the hole on April 25 through its space exploration mission Mars Express.
The crater is 30 kilometers wide, located in the planet's southern hemisphere.
The new image leads to a multitude of theories concerning the origin formation of eye-like shaped basin.
In addition to potential asteroid impacts, the ESA presumed that the region was once a landscape consisting of channels that carried water on the Martian surface about 3.5 to 4 billion years ago.
While there are other craters across the planet, the hole in question can be found in the Tantalus Fossae area where a group of long valleys called as "graben" are situated.
This area is located in the eastern side of the Alba Patera where the collision of faults leads rock to break, according to NASA.
Also Read: New Martian Crater Spotted on Mars (VIDEO)
Ancient Mars
The space community is still determining if Mars once hosted ancient life and a conducive environment for organisms.
NASA's Perseverance rover is one of the many manifestations of space technology that currently assesses if the Red Planet can sustain life, according to a study published in January 2017, as cited by Space.com.
The study's theory suggested that Mars may have contained an ocean in its northern hemisphere of the planet.
This is in addition to decades worth of geological evidence that Mars was once covered with lakes, ponds, rivers, and streams.
Scientists postulate that the planet had substantial liquid water level on its surface, according to the Scientific American, which also mentioned NASA's MAVEN spacecraft, which orbits Mars that a water depletion transpired due to atmospheric loss.
Related Article: Signs of Sustained Water Interaction Found in Mars' Jezero Crater
© 2025 NatureWorldNews.com All rights reserved. Do not reproduce without permission.





