During the upper Paleolithic era, a multicellular organism was frozen almost the time in history when humans first set foot into North America. About 24,000 years later, it has been found alive after sleeping for millenia.
This turned out to be a very huge discovery and might have changed the theory of how long organisms and perhaps humans can be presevered for generations.

Discovery of Bdelloid Rotifer
Bdelloid rotifer - a freshwater creature - is too tiny to see with the naked eye, measuring around 150 and 700 μm. The microorganism can be found in waters around the world. This animal survived being frozen for many years through a remarkable means of cloning itself multiple times through an asexual reproduction form called parthenogenesis, according to Accuweather.
This discovery, therefore, brought about questions on the reversible standstill lack of life theory or mechanism of the cryptobiosis.
These findings were done by researchers from the Soil Cryology Laboratory in Pushchino, Russia. It was discovered from a soil sample collected from a permafrost in northeastern Siberian.
This aged discovery was really surprising to the researcher as it felt really unbelievable that the animal was alive and doing well.
The permafrost sample of this creaature was collected from the Alazeya River, which flows from Siberia into the Arctic. Researchers also confirmed that there was no movement of the bdelloid rotifer due to the icy nature of the ground.
Research Findings
"The takeaway is that a multicellular organism can be frozen and stored as such for thousands of years and then return back to life - a dream of many fiction writers," Malvin, an author on this study stated.
He further talked about how big this discovery was and how it has totally changed the ideology of organism preservation.
This discovery might have been revolutionary and has added to the small number of organisms that have been found to be able to survive such extraordinary timespans but more are still yet to be uncovered.
The more complex an organism becomes, the more difficult it is to preserve alive, like in mammals, as per Smithsonian Magazine .
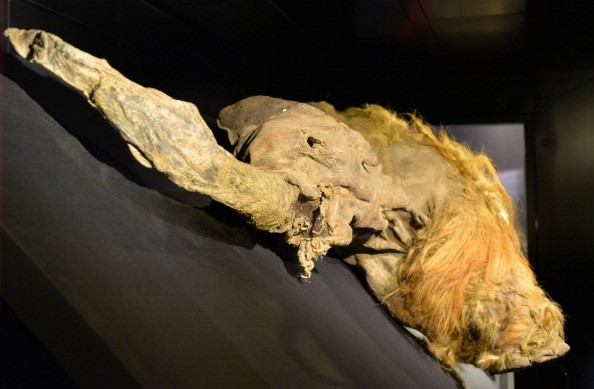
Other Organisms That Survived Extraordinary Timespans
In Russia, a pair of prehistoric nematodes, also called roundworms, were discovered and successfully revived, it is said to have been between 30,000 and 42,000 years old.
Studies have shown that over the years, a lot of organisms have been revived from their frozen state but what makes this new discovery more interesting is that none of these past organisms is as complex as the bdelloid rotifer.
Additionally, there have been discoveries on the dead but frozen larger species like the 20,000-year-old wooly rhino that was discovered by a Siberian farmer in the area of Yakutia in 2021 and the 57,000-year-old Pleistocene gray wolf puppy, the most perfectly preserved animal of its kind.
More research is still to be made on this study. The hope is that insights from these tiny animals will offer clues as to how better to cryo-preserve the cells, tissues, and organs of other animals, including humans.
Related Article : Melting of Arctic Permafrost Brings Long-dead Viruses Back
For more news, updates about microorganisms and similar topics don't forget to follow Nature World News!
© 2025 NatureWorldNews.com All rights reserved. Do not reproduce without permission.





