What is been implied if the Earth is under a geomagnetic storm warning? It may be a warning for disruptions yet to come and a signal for beautiful auroras.

National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA).
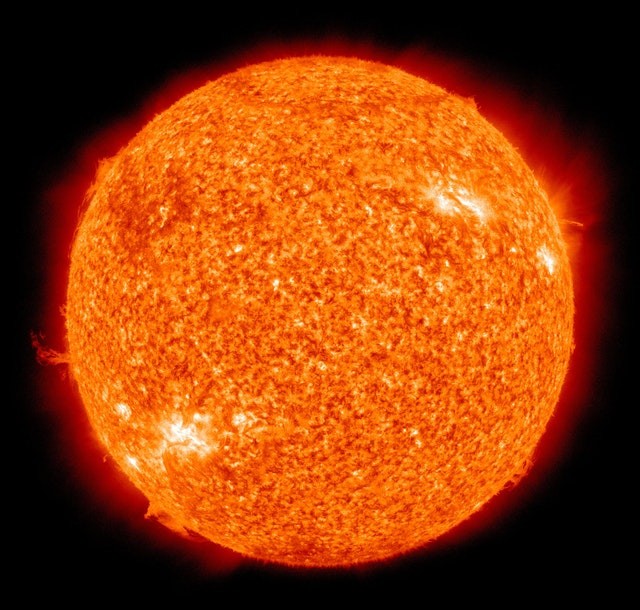
Last Sunday, there was a geomagnetic storm that placed a warning on the planet due to the "early arrival" of a coronal mass ejection (CME) that took place on the sun on April 22, according to the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA).
NASA explained the magnetosphere of the Earth shields us from solar particles. But when there is an emission of CME from the sun, it can lead to a disturbance in the magnetosphere of the Earth. This is the reason scientists often monitor space weather with the use of solar observatories.
"A billion tons or there about" of plasma from the sun gets to the Earth during CMEs, according to the NOOA. The forecast was for a G1-G2 Geomagnetic Storm in this case. Based on the Space Weather Scale of the agency, that would be a mild to average geomagnetic storm.
Unlike powerful geomagnetic storms that can lead to more serious disruptions like "widespread voltage control issues," geomagnetic storms that are milder have less intense impacts.
G2 Storms
G2 storms, for example, may provoke voltage alarms, and "long-duration" storms may likely lead to transformer damage. That said, people may even want to keep a record of such space weather forecasts due to the fact that they may affect or prompt the famous auroras.
NOAA said: "The transient solar wind characteristics is anticipated to bring about auroral enhancements that may be seen at night in the higher latitudes under sky conditions that are favorable.
So why would people want to view the space weather apart from the chance that such geomagnetic storms may bring about beautiful auroras?
Although the one that provoked the current warning was not intense, space weather may have an interaction with the Earth in potentially disruptive ways. As NASA gave an explanation, the modern technology that humans depend on today is quite unprotected to extreme space weather.
Global Navigation Satellite System (GNSS)
NOAA took into consideration that while the storms produce beautiful aurora, they also can disturb the navigation systems like the Global Navigation Satellite System (GNSS) and bring about risky geomagnetic induced currents (GICs) in the power grid and pipelines.
NASA noted that on March 13, 1989, geomagnetically induced currents that occurred due to CME caused a transformer failure that led to a blackout for more than nine hours, affecting over six million people.
In 2020, a study also investigated the possibility that a geomagnetic storm may have been one of the reasons for the sinking of the Titanic, possibly because the storm disturbed navigation and communication systems.
The effects of space weather were largely uncertain at the time. Solar activity and Earth's space environment can have detrimental effects on various technologies that modern society uses.
For more news, updates about geomagnetic storms and similar topics don't forget to follow Nature World News!
© 2025 NatureWorldNews.com All rights reserved. Do not reproduce without permission.





