Many years ago, 300 years approximately, vehicles didn't exist. People moved between locations on foot, and only the rich could afford to use carts that are pulled by horses. Today, the narrative has changed. Vehicles have become so commonplace that it's now a crucial part of our daily lives. The earliest automobiles were steam-powered, but the world has moved on with the more versatile internal combustion engines. In this post, we will be discussing the core components that make up your car's engine.
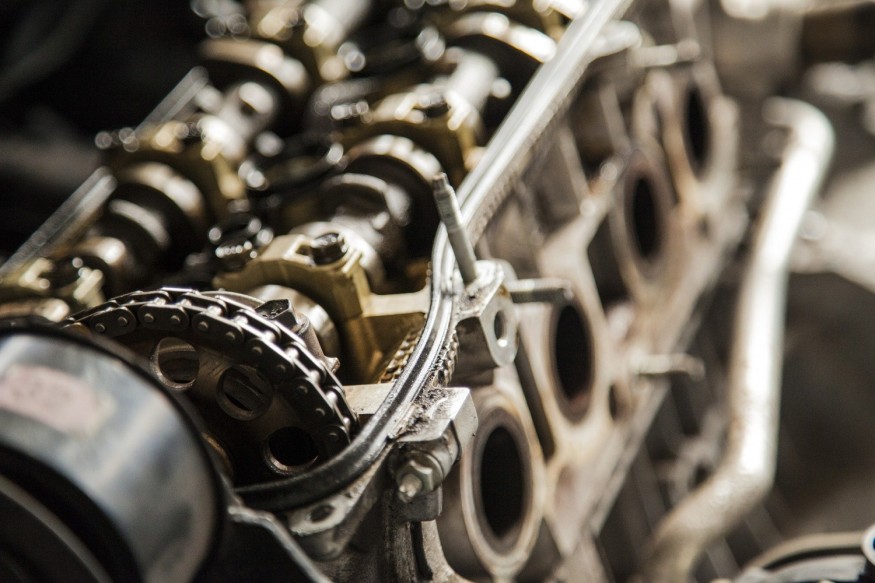
Camshaft
As stated earlier, your car's engine is an internal combustion engine. For it to work, fuel and air (oxygen) ignite in tiny little sparks. These sparks occur multiple times over inside the cylinder in the form of a controlled explosion. Through these "controlled explosions," energy is produced, which is eventually converted into motion. The camshaft is a critical component that ensures all of this action happens inside a combustion engine.
Wikipedia defines a camshaft simply as "a shaft to which a cam is fastened or which a cam forms an integral part of." The camshaft is no more than a length of rod or shaft. It has shaped lobes positioned along with it, and these lobes are called cams. When the engine runs, the shaft rotates, and with every rotation of the shaft, the cam creates an impact on a valve. (The valve controls the amount of air and gas mixture that's allowed into the cylinder). The severity of this impact is determined by the shape of the cam and the speed of rotation controlling the rate of action.
As the camshaft performs this function, it determines how efficient your vehicle's engine will be. Consequently, a faulty camshaft will make your car act in a variety of unpleasant ways. A faulty camshaft will cause your car to stop or stall frequently. It can also cause a reduction in gas mileage. The good news is you can get your camshafts replaced with spares at gold farb inc products or any trusted automobile service center.
Injection Pump
Your car has a fuel delivery system. This system guarantees the transportation of fuel from the fuel tank to the engine. The injection pump is an integral part of this system. (Discussion of the other components will follow in the next paragraphs). The injection pump practically "injects" fuel into the combustion chamber. Without the injection pump, the combustion cylinders will get no fuel. An absence of this means no "controlled explosions" that create energy will take place.
The injection pump supplies fuel to the combustion chamber that's then dispersed around the combustion chamber in the form of pressurized fuel (gas). On entry into fuel injector, the pressurized fuel heads into a plunger, which prepares the fuel for the final exit. A spray tip distributes the fuel as a fine mist after the fuel leaves the fuel injector. The injection pump, traditionally, is driven indirectly from the crankshaft by gears, chains, or a toothed belt, which also drives the camshaft.
The performance of your engine is closely tied to the performance of the fuel injection pump. If it comes down with any fault, your car will starve to death. This makes fuel injection problems one of the most pressing engine issues to deal with.
Many fuel injector failure problems can be traced to either of two causes: a faulty mechanical problem in the physical fuel injector housing or the use of low-quality fuel. These two issues are the foundation on which other problems rest. You should avoid running your engine on contaminated fuel, and make sure your fuel tank is always at least half-full.
Also, ensure your injection pump is regularly serviced. Problems such as the presence of a foreign object inside the injector or injector's bad timing will be promptly identified and resolved. Replacing your fuel filter after every 40,000 miles also prevents you from any unexpected malfunctioning of the injection pump.
Fuel Injector
The fuel injector is another component of your vehicle engine's fuel delivery system. It receives and transfers fuel into the engine in the form of a high-pressure mist. It's controlled by your vehicle's engine computer. This allows it to optimize the amount of fuel the engine gets, and also to control the timing of the fuel injection. There's always one fuel injector per cylinder that delivers fuel to the engine. It works alongside the injector pump.
The fuel injector also does the job of regulating the amount of fuel that enters the intake of a vehicle. It gets an electrical signal from the engine sensor that comes from the Power-train Control Module (PCM). Through this process, the fuel injector can dictate the duration for which it stays open and how much fuel is allowed to pass through.
Fuel injectors are usually very dependable and rarely go bad. However, they tend to develop faults every once in a while. Signs your vehicle is suffering from a faulty fuel injector include vehicle misfire and rough starts during ignition. You should also take note of incidents where your vehicle loses power incessantly or accelerates with discomfort.
Plunger
The plunger is another crucial component of your vehicle's fuel delivery system. What the plunger does is to control the quantity of fuel that enters the injector. At the same time, it regulates the timing interval for each fuel injection. Each cylinder in your vehicle's engine has a corresponding plunger. Each one is responsible for transferring the fuel mixture through the injector nozzle. Like the injection pump, it's also driven by the crankshaft of the engine.
Modern engines are built with an Engine Control Unit (ECU) that monitors the amount of fuel that enters the injector. The injector is built with a solenoid that enables the ECU to determine the injector times accurately. This is one by monitoring inputs from the oxygen sensor and the engine speed. Your vehicle's fuel efficiency is dependent on the proper working of the fuel injection system.
If the diesel plunger is damaged, it shows signs synonymous with any of the other fuel injection system parts - the fuel injector and the injector pump. A faulty plunger could cause problems with your car's efficiency and fuel consumption. You should replace the plunger if it's damaged to minimize any possible damage to your car's engine and fuel ignition system.
Turbo Charger
A turbocharger is a turbine-driven device that increases an internal combustion engine's efficiency. The turbocharger creates more power output by forcing extra compressed air into the combustion chamber. For the turbocharger to achieve this, it spins the air pump using the exhaust. The pump, in turn, pushes the entire extra air into your engine's cylinder. This allows your engine to work at higher horsepower.
The turbocharger is an innovation that automobile engineers designed. It allows the engine to generate more power. The other alternative is to fit the vehicle with an extra engine that comes at great cost.
Turbochargers are supposed to be long-lasting. However, it may come to some damage over time. Richard Reed identifies the signs of a weak turbocharger as slow acceleration, burning oil, and excessive exhaust smoke. Often, these faults occur as a result of cracks, wear and tear, and carbon deposits. To prevent an accumulation of carbon deposits, ensure the oil is changed frequently. Replacing old turbochargers with new ones solves the problem of wear and tear.
Nozzles
The fuel injector nozzle is critical to the performance and emissions of your vehicle's engines. According to a paper published on DieselNet Technology guide, some of the important injector nozzle parameters, including details of the injector seat, the injector sac, and nozzle-hole size and geometry, affect the combustion characteristics of the diesel engine. It also impacts on the stability of the emissions and performance throughout the lifetime of the engine and the mechanical durability of the injector.
The design of the diesel fuel injector nozzle is critical to the performance and emissions of modern diesel engines. Some of the essential injector nozzle design parameters include details of the injector seat, the injector sac, and nozzle-hole size and shape. These features not only affect the combustion characteristics of your engine. These also affect the stability of the emissions and performance over the lifetime of the engine and the mechanical durability of the injector.
When the injection valve is faulty or not working as intended, you begin to experience problems starting your car. There will also be an increase in fuel consumption, an incessant loss of power, and a fluctuating idle speed. A faulty nozzle can bring serious damage to your car's engine or reduce the engine's service life.
The cause of faulty injection valves is quite a handful. Contaminated fuel, short circuit coil, or a break in the cable control unit are possible causes of a faulty injection valve. While it's possible to fix a faulty injection valve by yourself, if you're not experienced with vehicle parts, it's advised that you seek the services of a professional car mechanic.
© 2025 NatureWorldNews.com All rights reserved. Do not reproduce without permission.





